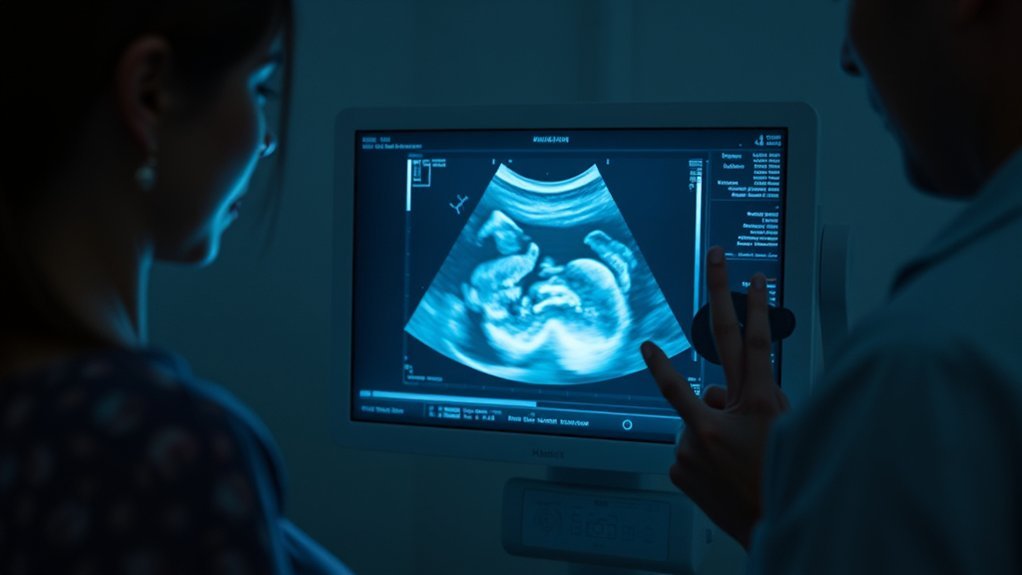
The NT scan is more than just a routine ultrasound; it’s a critical assessment of your baby’s health. While the procedure itself won’t produce symptoms or signs, it plays a pivotal role in screening for potential chromosomal conditions. Understanding what to expect before, during, and after the scan can help ease your concerns. So, what should you know about the timing, procedure, and results of this important test?
Understanding the NT Scan: Purpose and Procedure
When you’re expecting a baby, understanding the NT scan—short for nuchal translucency scan—can be essential for evaluating your child’s health.
This non-invasive ultrasound is typically performed between 11 weeks 0 days and 13 weeks 6 days of pregnancy (often when the crown–rump length is about 45–84 mm). It measures the fluid at the back of your baby’s neck, which can indicate the risk of chromosomal conditions, such as Down syndrome, and may also be considered with risks for trisomy 18 and trisomy 13.
During the procedure, you’ll lie on an exam table while a technician applies gel to your abdomen and uses a transducer to capture images. The scan usually takes about 20 minutes.
Although it’s a routine part of prenatal care, your healthcare provider will discuss the results and any follow-up testing, ensuring you feel supported and informed throughout the process.
Timing of the NT Scan: When to Schedule
Timing is vital when scheduling your NT scan, as the ideal window is typically between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy.
Early detection of potential issues can greatly impact your care and decision-making moving forward.
In the U.S., prenatal genetic screening options (serum screening with or without NT ultrasound, or cell-free DNA screening) and diagnostic testing (CVS or amniocentesis) are offered to all pregnant patients regardless of age or baseline risk. It’s important to coordinate with your healthcare provider to guarantee you receive this important screening at the right time.
Optimal Week for Scheduling
Scheduling your NT scan at the right time is essential for obtaining accurate results and ensuring a thorough assessment of your baby’s health.
The best window for this scan is typically between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation. During this period, your healthcare provider can measure the nuchal translucency, which is the fluid at the back of your baby’s neck. This measurement helps assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome.
It’s important to schedule the scan within this timeframe to maximize the accuracy of the results. If you’re unsure about scheduling, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for guidance. They’ll help you find a suitable appointment that aligns with your pregnancy journey.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection plays a pivotal role in managing your pregnancy effectively. Scheduling your NT scan between 11 and 14 weeks allows for the timely assessment of potential chromosomal abnormalities.
By identifying any risks early on, you can explore further diagnostic options and make informed decisions about your pregnancy. This proactive approach not only helps you understand your baby’s health but also provides peace of mind during a critical time.
Early detection means you can better prepare emotionally and physically for any challenges that may arise. Remember, the sooner you know, the better equipped you’ll be to discuss your options with your healthcare provider, ensuring a supportive and informed pregnancy journey.
Prioritize your NT scan to safeguard your and your baby’s well-being.
What to Expect During the NT Scan
When you arrive for your NT scan, you’ll find that the process is straightforward and designed to guarantee your comfort.
You’ll first be welcomed by a healthcare professional who’ll explain the procedure in detail. After that, you’ll lie down on an examination table, and a gel will be applied to your abdomen. This gel helps the ultrasound probe make better contact with your skin.
The technician will then use the ultrasound device to capture images of your baby’s neck, measuring the nuchal translucency. The scan typically lasts about 20 to 30 minutes.
Throughout the process, you can ask questions, and the technician will keep you informed. It’s normal to feel a mix of emotions, and your comfort is a priority during this important assessment.
Interpreting NT Scan Results
Interpreting the results of your NT scan can feel overwhelming, but understanding the findings is vital for your prenatal care.
Your healthcare provider will usually explain whether the measurements are within normal ranges or if there are any concerning indicators. A higher nuchal translucency measurement might suggest an increased risk for chromosomal abnormalities, but it doesn’t guarantee a diagnosis.
It’s important to remember that this test is a screening tool, not a definitive one. If your results indicate a higher risk, your doctor may recommend further testing, like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS). When an enlarged NT is identified, guidelines also support offering genetic counseling and planning for a detailed ultrasound exam around 18–22 weeks to assess for structural differences.
Always feel free to ask questions; being informed helps you make the best decisions for you and your baby’s health.
Common Symptoms and Signs Leading to NT Scan
Many expectant parents may wonder when to contemplate an NT scan. Typically, you’ll consider this screening between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy. In the U.S., prenatal genetic screening is offered to all pregnant patients (not only those with specific risk factors), so you can discuss it with your provider regardless of age or history.
Common signs that may prompt you to discuss an NT scan with your healthcare provider include advanced maternal age, a family history of genetic disorders, or previous pregnancies with chromosomal abnormalities.
Signs to discuss an NT scan with your provider include advanced maternal age, family history of genetic disorders, or past chromosomal abnormalities in pregnancies.
You might also experience heightened anxiety about potential risks, which is normal. Additionally, if you’ve undergone any abnormal screenings during your first trimester, your doctor may recommend this scan for more clarity.
The NT scan measures nuchal translucency, which can indicate the risk of certain genetic conditions, helping you make informed decisions about your pregnancy.
Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice tailored to your situation.
Factors Affecting NT Scan Results
Several factors can influence your NT scan results, and it’s important to understand them.
Maternal age, fetal position, and the skill of the ultrasound technician all play critical roles in the accuracy of the measurements.
Being aware of these factors can help you have a more informed conversation with your healthcare provider about your results.
Maternal Age Impact
As you approach the NT scan, it’s vital to understand how maternal age can markedly influence the results.
Women over 35 tend to have a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities, which can affect the measurements taken during the scan. The nuchal translucency thickness is often interpreted in conjunction with maternal age; older mothers may show different risk profiles.
This doesn’t mean that younger mothers are exempt from concerns, but the data generally indicates a heightened risk for older expectant mothers.
It’s important to discuss your individual risk factors with your healthcare provider, who can offer tailored advice and support.
Fetal Position Influence
Fetal position plays a significant role in the accuracy of the NT scan results. When your baby is in a favorable position, it enhances the technician’s ability to measure the nuchal translucency accurately.
If your baby is curled up or facing away, it can obstruct clear views, leading to less reliable measurements. This positioning can sometimes result in false positives or negatives, creating unnecessary anxiety.
You may feel reassured knowing that many factors, including the fetal position, are temporary and can change throughout the scan. If your baby’s position isn’t ideal, your technician might recommend repositioning or waiting for a moment to see if the baby shifts.
It’s crucial to remain calm, as these variations are common and generally manageable.
Ultrasound Technician Skill
The skill of the ultrasound technician greatly impacts the accuracy of NT scan results. Their expertise guarantees proper measurement of the nuchal translucency, which is vital for evaluating potential chromosomal abnormalities. Factors like technique, experience, and communication can influence outcomes considerably.
| Factor | Impact on Results | Importance Level |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Technique | Precise measurements are essential | High |
| Equipment Quality | High-quality machines yield better images | Medium |
| Technician Experience | More experience leads to accuracy | High |
| Patient Interaction | Comfort can improve cooperation | Medium |
As you prepare for your NT scan, remember that a skilled technician can enhance the overall accuracy, providing you with more reliable insights about your pregnancy.
Next Steps After the NT Scan
Once you’ve completed your NT scan, it’s essential to understand the next steps in your prenatal journey. You’ll receive results that may indicate your baby’s risk for certain chromosomal conditions.
If your results suggest a higher risk, your healthcare provider might recommend further testing, such as a chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis. These tests can provide more definitive information but come with their own risks.
It’s critical to discuss these options thoroughly with your provider, considering both the benefits and potential implications. Regardless of the results, maintaining regular prenatal check-ups is important for monitoring your health and your baby’s development.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can the NT Scan Detect All Genetic Disorders?
The NT scan can’t detect all genetic disorders. It primarily screens for specific chromosomal abnormalities, like Down syndrome. For a thorough assessment, you might consider additional testing options, discussing them with your healthcare provider.
Is It Safe for Both Mother and Baby?
Yes, when performed by trained professionals, the NT scan (diagnostic ultrasound) is generally considered safe for both you and your baby and uses sound waves—not ionizing radiation. As a screening test, it does not diagnose conditions or have a fixed “accuracy rate”; detection varies by the screening approach used.
How Does the NT Scan Differ From Other Tests?
The NT scan specifically measures nuchal translucency via ultrasound to help evaluate risk for chromosomal abnormalities. The first-trimester combined screening pairs this ultrasound with blood tests (PAPP-A and free β-hCG) to estimate risk. Cell-free DNA (cfDNA/NIPT) is a blood test available from about 10 weeks that is more sensitive for common trisomies. Diagnostic tests—CVS (typically 10–13 weeks) and amniocentesis (typically ≥15 weeks)—can provide definitive results.
Will I Need to Prepare Differently for the Scan?
You won’t need extensive preparation for the scan. Many clinics allow you to eat normally; some ask you to arrive with a moderately full bladder to improve images—follow your clinic’s instructions.
What if I Miss My Scheduled NT Scan Appointment?
If you miss your scheduled NT scan appointment, contact your healthcare provider immediately. After about 13 weeks 6 days, the NT measurement may no longer be feasible; your provider may offer alternatives such as cell-free DNA screening (from 10 weeks onward) or the second-trimester quad screen (typically 15–22 weeks).
Conclusion
To summarize, while the NT scan itself doesn’t produce symptoms or signs, it plays an essential role in evaluating your baby’s health. You might wonder if experiencing certain pregnancy symptoms could affect your results, but rest assured, the scan focuses solely on measuring nuchal translucency. Understanding this can ease your mind as you navigate your pregnancy. If any concerns arise from your results, discussing them with your healthcare provider will help you make informed decisions moving forward.