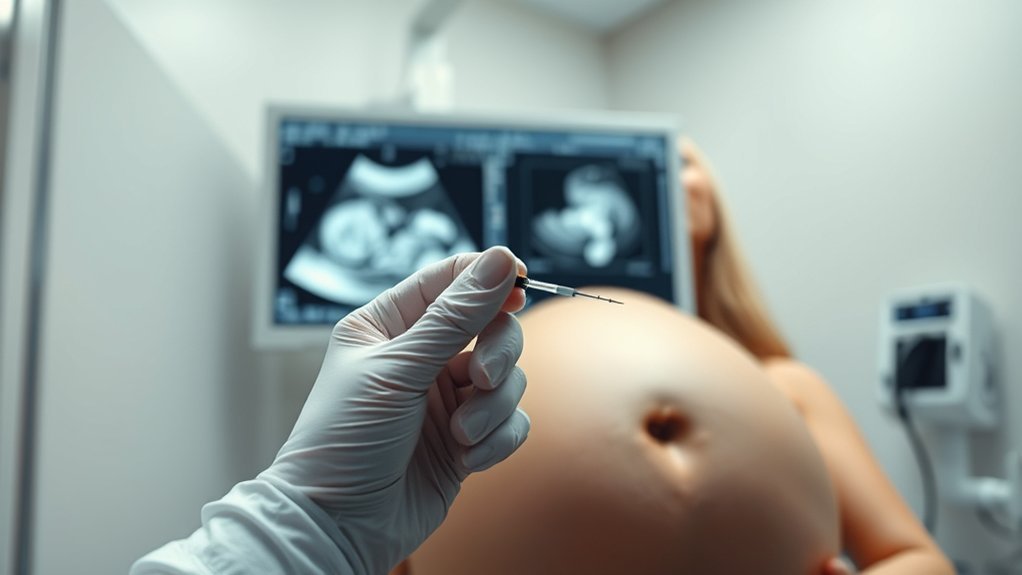
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) is a essential procedure, a significant tool for early genetic screening, and an important option for high-risk pregnancies. If you’re over 35, have a family history of genetic disorders, or received abnormal screening results, you might be considering CVS. Understanding why it’s recommended and the factors that contribute to these decisions can help you navigate your options. Let’s explore the causes and risk factors associated with CVS in the U.S.
Understanding Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) is a prenatal testing procedure that allows you to detect certain genetic conditions in your baby early in pregnancy. Typically performed between the 10th and 13th weeks, CVS involves taking a small sample of the placenta’s tissue. This sample contains chorionic villi, which share your baby’s genetic makeup.
The procedure can be done through your abdomen or cervix, depending on your situation. CVS provides results faster than other tests, often within a week.
While it’s a valuable tool for evaluating genetic disorders, it’s not without risks, such as miscarriage or infection. Understanding CVS can help you make informed decisions about your pregnancy and potential follow-up testing or care.
Indications for Performing CVS
If you’re considering chorionic villus sampling (CVS), it’s important to understand when this procedure is recommended.
It’s often performed for genetic disorder screening, especially if there’s a family history of such conditions.
Additionally, maternal age plays a significant role, as older mothers may be at higher risk for chromosomal abnormalities.
Genetic Disorder Screening
When you’re considering genetic disorder screening during pregnancy, chorionic villus sampling (CVS) can be a valuable option. This procedure allows you to detect certain genetic conditions early in the pregnancy, typically between the 10th and 13th weeks.
CVS is particularly recommended if you have a family history of genetic disorders, abnormal results from earlier screenings, or if you’re a carrier of specific genetic conditions. It can identify conditions like Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, and Tay-Sachs disease.
The results can help you make informed decisions about your pregnancy. However, it’s essential to discuss the benefits and risks with your healthcare provider to determine if CVS is the right choice for you.
Maternal Age Considerations
As you navigate your pregnancy journey, maternal age plays a crucial role in evaluating whether to undergo chorionic villus sampling (CVS). Women aged 35 and older are often advised to contemplate CVS due to an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome. This age threshold reflects the heightened risk associated with advanced maternal age.
If you’re over 40, your healthcare provider may strongly recommend CVS to gather essential genetic information early in your pregnancy. Additionally, if you have a family history of genetic disorders, your age further influences the decision-making process.
Ultimately, discussing your specific circumstances with your healthcare provider will help you determine the best course of action for your pregnancy and peace of mind.
Advanced Maternal Age as a Risk Factor
If you’re over the age of 35, you’re considered to have advanced maternal age, which can increase genetic risks for your baby.
This age factor often leads to recommendations for more thorough screening, including chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Understanding these risks can help you make informed decisions during your pregnancy.
Definition of Advanced Maternal Age
Advanced maternal age refers to the age of a pregnant woman, typically defined as 35 years or older at the time of delivery. This age threshold has become significant in prenatal care discussions, as it may impact various aspects of pregnancy and delivery.
| Age Range | Common Considerations | Resources Available |
|---|---|---|
| Under 35 years | Generally lower risk | Standard prenatal care |
| 35-39 years | Increased monitoring needed | Genetic counseling services |
| 40 years and up | Higher risk assessments | Specialized maternal care |
Understanding advanced maternal age helps you make informed decisions about prenatal testing, such as chorionic villus sampling, ensuring you receive the appropriate care tailored to your specific needs.
Impact on Genetic Risks
When considering pregnancy, the age of a mother can considerably influence the genetic risks for her child.
As you age, particularly beyond 35, the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities increases. Conditions like Down syndrome and other genetic disorders are more common in babies born to older mothers. This heightened risk stems from the aging of eggs, which can lead to errors during cell division.
Additionally, older mothers may face a higher chance of miscarriage, further complicating genetic outcomes.
It’s essential to understand these risks when planning your pregnancy. Being aware allows you to make informed decisions and discuss potential screening options with your healthcare provider, ensuring you have the best possible information for your family’s health.
Screening Recommendations for Older Mothers
As maternal age increases, so do the recommendations for genetic screening to detect potential abnormalities. For women over 35, healthcare providers often suggest additional screenings, including non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) and chorionic villus sampling (CVS). These tests help identify chromosomal conditions like Down syndrome or trisomy 18.
Here’s a quick overview of screening options:
| Age Group | Recommended Tests | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Under 35 | Routine Ultrasound | General health assessment |
| 35-40 | NIPT & CVS | Detect chromosomal abnormalities |
| Over 40 | CVS & Amniocentesis | Confirm genetic conditions |
Adhering to these screening recommendations can help you make informed decisions about your pregnancy and care.
Family History of Genetic Disorders
Having a family history of genetic disorders can markedly influence your decision to undergo chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
If you or your partner have relatives with conditions such as cystic fibrosis, Down syndrome, or sickle cell anemia, you might consider CVS to assess your baby’s risk for these disorders. This test allows for early detection, enabling you to make informed choices about your pregnancy.
It’s essential to discuss your family’s medical history with your healthcare provider, who can help evaluate your risk factors and guide you through the decision-making process.
Understanding the implications of genetic disorders can provide peace of mind, helping you prepare for potential outcomes, both positive and challenging, as you move forward with your pregnancy.
Abnormal Screening Test Results
If your screening tests show abnormal results, it’s essential to discuss the implications with your healthcare provider. Understanding these results can help you make informed decisions about further testing, like chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Here are some important points to evaluate:
- Follow-Up Testing: Your provider may recommend additional tests to confirm any findings.
- Genetic Counseling: You might benefit from speaking with a genetic counselor to understand your options.
- Risk Assessment: Abnormal results can indicate potential genetic conditions, but not every abnormality means there’s a problem.
- Support Resources: Look into support groups or resources to help you navigate this emotional journey.
Being proactive and informed will empower you as you move forward.
Previous Pregnancy Complications
Previous pregnancy complications can greatly impact your current pregnancy planning and decisions. If you’ve experienced issues like preterm birth, gestational diabetes, or preeclampsia, you might face increased risks in future pregnancies.
These complications can influence your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding tests and monitoring, including whether chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is necessary. It’s essential to discuss your pregnancy history with your doctor, as they’ll evaluate how past issues might affect your current situation.
They may suggest additional screenings or precautions based on your specific circumstances. Remember, being informed and proactive about your health can help guarantee a healthier pregnancy journey.
Always seek guidance tailored to your unique needs and history for the best outcomes.
Genetic Carrier Screening
Genetic carrier screening is essential for identifying potential risks of passing on genetic disorders to your children.
By understanding your carrier status, you can make informed decisions about your family planning.
Common genetic disorders detected through screening include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and Tay-Sachs disease.
Importance of Genetic Testing
Why is genetic testing, specifically genetic carrier screening, so essential for expectant parents? This process helps you understand your risk for passing on genetic disorders to your child.
Here are four key reasons why it’s important:
- Informed Decisions: You can make better choices regarding your pregnancy and potential interventions.
- Early Detection: Identifying risks allows for early planning and management of any conditions.
- Family Planning: Understanding carrier status helps you and your partner discuss future pregnancies and options available.
- Emotional Preparedness: Knowing the risks can help you emotionally prepare for any outcomes, reducing anxiety.
Genetic carrier screening is a critical step in ensuring the health and well-being of your future child.
Common Genetic Disorders Identified
When it comes to genetic carrier screening, several common disorders can be identified, helping parents understand potential risks. You might find conditions like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and Tay-Sachs disease on the list. These disorders often have a genetic basis, meaning they can be passed down from parents to children.
If you or your partner are carriers, it can greatly influence family planning decisions. Other disorders include spinal muscular atrophy and hemoglobinopathies. Identifying these risks early allows you to explore options, including further testing or counseling.
Knowing your carrier status helps you make informed choices about your health and your baby’s future. Understanding these genetic disorders is an essential step in prenatal care.
Ethical Considerations in CVS
As you consider chorionic villus sampling (CVS), it’s important to weigh the ethical implications involved in the procedure.
CVS raises several concerns that you should keep in mind:
- Informed Consent: You need to guarantee that you fully understand the procedure and its potential outcomes before making a decision.
- Parental Rights: Consider the ethical implications of knowing genetic information and how it may affect your decisions regarding the pregnancy.
- Discrimination Risks: There’s a possibility that genetic information could lead to discrimination against the child, impacting their future opportunities.
- Emotional Impact: The knowledge gained from CVS may lead to difficult emotional decisions, including the potential for termination based on test results.
Understanding these factors can help you navigate the complexities of CVS.
Potential Risks and Complications of CVS
While chorionic villus sampling (CVS) can provide valuable genetic information, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks and complications associated with the procedure.
One of the primary risks is the chance of miscarriage, which occurs in about 1 in 100 cases. You might also experience cramping or spotting after the procedure.
One significant risk of CVS is miscarriage, occurring in approximately 1 in 100 cases, along with potential cramping or spotting.
In rare instances, CVS can cause infection or injury to the fetus or placenta. Additionally, there’s a small risk of developing Rh sensitization if you’re Rh-negative and haven’t received the necessary treatment.
Understanding these risks can help you make informed decisions about whether CVS is the right choice for you. Always discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider to guarantee you’re fully informed.
Making Informed Decisions About CVS
Making informed decisions about chorionic villus sampling (CVS) involves understanding both the procedure and your unique circumstances.
It’s essential to weigh the benefits and risks before proceeding. Here are four key factors to evaluate:
- Medical History: Review any previous pregnancies or genetic conditions that might affect your decision.
- Test Purpose: Understand why you’re contemplating CVS, such as screening for specific genetic disorders.
- Timing: Know the ideal time during pregnancy for CVS, typically between 10 to 13 weeks.
- Consultation: Discuss your options with a healthcare provider who can provide personalized advice based on your situation.
These evaluations will empower you to make the best choice regarding CVS for your pregnancy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Is CVS Different From Amniocentesis?
CVS involves taking a sample from the placenta early in pregnancy, usually between 10-13 weeks, while amniocentesis occurs later, around 15-20 weeks, and samples amniotic fluid. Both tests check for genetic conditions.
What Is the Optimal Timing for CVS During Pregnancy?
You should consider having CVS between the 10th and 13th weeks of pregnancy. This timing allows for early detection of genetic disorders while minimizing risks associated with the procedure. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Can CVS Determine All Genetic Disorders?
You can’t judge a book by its cover; CVS can detect many genetic disorders, but it doesn’t identify every condition. It’s essential to discuss limitations and additional testing options with your healthcare provider for thorough insights.
How Accurate Are CVS Results Compared to Other Tests?
CVS results are highly accurate, typically around 98-99%, which is comparable to amniocentesis. However, non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is also reliable, though it can’t provide a definitive diagnosis like CVS can.
What Should I Expect During the CVS Procedure?
During the CVS procedure, you’ll feel slight discomfort as a thin needle or catheter collects tissue from the placenta. It’s quick, usually taking only 10-15 minutes, and you can expect some cramping afterward.
Conclusion
In the journey of parenthood, Chorionic Villus Sampling shines like a guiding star, illuminating the path to understanding genetic risks. By recognizing advanced maternal age, family history, and abnormal screenings, you can make informed choices that protect your future. Just as a compass directs sailors through stormy seas, CVS empowers you to navigate the complexities of genetic health. Embrace the knowledge it offers, ensuring a brighter horizon for your family as you step into this new chapter of life.