Many people believe that amniocentesis is only for high-risk pregnancies, but this isn’t always the case. Understanding the purpose, procedure, and potential outcomes can help clarify its role in prenatal care. If you’re considering this test, you might have questions about its timing, risks, and the information it can provide. Let’s explore these important aspects together.
What Is Amniocentesis?
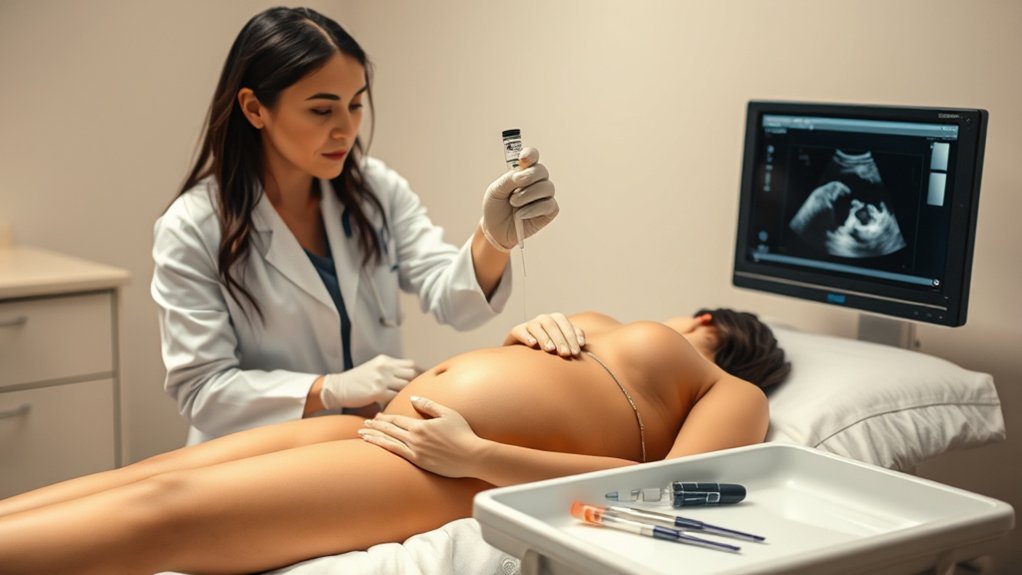
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used to collect amniotic fluid surrounding a fetus in the womb. During this procedure, a thin needle is inserted through your abdomen and into the amniotic sac to extract a small volume of fluid. This fluid contains fetal cells and various substances, providing valuable information about the fetus’s health.
You’ll typically undergo amniocentesis between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy. The procedure is performed under ultrasound guidance to guarantee safety and accuracy.
While it carries some risks, such as infection or miscarriage, it’s often considered when specific genetic or chromosomal conditions are suspected. Understanding what amniocentesis entails helps you make informed decisions regarding prenatal testing and fetal health monitoring.
When Is Amniocentesis Recommended?
Amniocentesis is often recommended if you’re of advanced maternal age, as the risk of chromosomal abnormalities increases.
It may also be suggested if you have a family history of genetic disorders or if you’ve experienced anomalies in previous pregnancies.
Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your prenatal care.
Advanced Maternal Age
As you reach advanced maternal age, typically defined as 35 years or older, your healthcare provider may recommend amniocentesis to assess potential genetic abnormalities in your unborn child.
This procedure can provide valuable information, helping you make informed decisions about your pregnancy.
Here are some reasons why amniocentesis might be recommended:
- Increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
- Family history of genetic disorders.
- Abnormal results from earlier prenatal screening tests.
- Concerns about maternal health conditions that may affect the fetus.
Genetic Disorder Risk
How can you determine if amniocentesis is right for you when considering the risk of genetic disorders?
If you’re at increased risk for conditions like Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, or spina bifida, your healthcare provider might recommend amniocentesis. This procedure is typically offered between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy, allowing for early detection of chromosomal abnormalities.
You may also consider it if non-invasive tests indicate a higher risk. Discuss your family history and any abnormal screening results with your provider to assess your specific situation.
Ultimately, the decision should be based on your comfort level with the potential risks and benefits, including the risk of miscarriage associated with the procedure. Your healthcare provider can help guide you through this important choice.
Previous Pregnancy Anomalies
If you’ve experienced previous pregnancy anomalies, discussing amniocentesis with your healthcare provider may be essential. This procedure can help assess the risk of genetic disorders in your current pregnancy.
Here are some situations where amniocentesis is often recommended:
- History of Genetic Disorders: If you or your partner have a family history of genetic conditions.
- Previous Chromosomal Abnormalities: If your previous pregnancy had chromosomal issues, this test can provide insight for the current one.
- Maternal Age: If you’re over 35, the risk of anomalies increases, making amniocentesis a viable option.
- Abnormal Ultrasound Findings: If your ultrasound suggests potential anomalies, amniocentesis can clarify these concerns.
Consult your provider to understand the benefits and risks associated with this procedure.
How Is the Procedure Performed?
During amniocentesis, a thin, sterile needle is carefully inserted through the abdominal wall into the amniotic sac surrounding the fetus.
Your healthcare provider will first clean your abdomen with an antiseptic solution to minimize infection risk. You’ll typically lie on your back, and an ultrasound may be performed to locate the fetus and the amniotic fluid.
Once the site is identified, the needle is inserted, and a small amount of amniotic fluid is withdrawn for testing. This process usually takes about 30 minutes, and you may feel some pressure or mild discomfort.
After the procedure, you’ll be monitored for a short time to guarantee your safety before you can go home.
What Information Can Amniocentesis Provide?
Amniocentesis can provide essential information about your baby’s health.
It allows for the detection of genetic disorders, helping you understand potential risks.
Additionally, it offers insights into fetal lung development, which can be vital for planning any necessary interventions.
Genetic Disorders Detection
One of the primary benefits of amniocentesis is its ability to detect genetic disorders in the developing fetus. By analyzing the amniotic fluid, you can gain critical insights into your baby’s health.
Here are some genetic conditions that amniocentesis can help identify:
- Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) – A condition caused by an extra chromosome that affects physical and intellectual development.
- Edward syndrome (Trisomy 18) – A serious genetic disorder that can lead to severe developmental issues and short life expectancy.
- Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13) – A complex condition associated with severe intellectual disability and numerous physical abnormalities.
- Cystic fibrosis – A hereditary disorder affecting the lungs and digestive system.
Detecting these disorders allows for informed decision-making during pregnancy.
Fetal Lung Development Insights
While evaluating fetal health, understanding lung development is fundamental, and amniocentesis can provide valuable insights into this area. This procedure analyzes amniotic fluid for surfactant levels, which are essential for lung maturation.
By measuring the lecithin-to-sphingomyelin (L/S) ratio, you can assess fetal lung readiness for breathing outside the womb. An ideal L/S ratio indicates sufficient surfactant production, suggesting a lower risk of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) after birth. If the ratio is low, it may indicate immature lungs, prompting further monitoring and potential interventions.
Additionally, amniocentesis can help identify other conditions that may affect lung development, allowing for a thorough evaluation of fetal health. This information is critical for making informed decisions about delivery and neonatal care.
What Are the Risks Involved?
Understanding the risks involved with amniocentesis is essential for making an informed decision. While this procedure can provide valuable information about your baby’s health, it does come with certain risks.
Understanding the risks of amniocentesis is crucial for making an informed choice about your baby’s health.
Here are some potential complications to evaluate:
- Miscarriage: There’s a small risk (about 1 in 300 to 1 in 500) of miscarriage following the procedure.
- Infection: There’s a slight chance of introducing an infection into the uterus.
- Amniotic Fluid Leakage: You might experience a leakage of amniotic fluid, which could pose risks to the pregnancy.
- Needle Injury: Although rare, there’s a possibility of injury to the fetus or placenta from the needle.
Discuss these risks with your healthcare provider to weigh your options effectively.
What Are the Benefits of Amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis offers several significant benefits that can aid in evaluating your baby’s health. This procedure provides essential information about genetic disorders, allowing you to make informed decisions regarding your pregnancy. Additionally, it can assess fetal lung maturity, which is important if early delivery is considered.
| Benefit | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Testing | Identifies chromosomal abnormalities | Guides prenatal care decisions |
| Fetal Lung Maturity | Measures surfactant levels in amniotic fluid | Helps prepare for potential early delivery |
| Information on Infections | Detects infections affecting the fetus | Guarantees timely treatment options |
How Should Parents Prepare for the Procedure?
To guarantee a smooth amniocentesis experience, parents should take several preparatory steps. Proper preparation can help reduce anxiety and ascertain the procedure goes as planned.
Here are four essential steps to contemplate:
- Discuss Concerns: Talk with your healthcare provider about any questions or concerns regarding the procedure.
- Understand Instructions: Follow any specific instructions related to food and fluid intake before the appointment.
- Arrange Support: Organize for a support person to accompany you, as emotional support can be beneficial.
- Prepare for Recovery: Plan for rest after the procedure, allowing time for recovery and any follow-up appointments.
Being prepared can considerably enhance the overall experience and help you feel more in control during this important time.
What Can Be Expected After Amniocentesis?
After the amniocentesis, it’s normal to have questions about what comes next. You might experience mild cramping, spotting, or discharge, which usually resolves within a few days.
It’s crucial to monitor for any severe pain, heavy bleeding, or signs of infection, such as fever or chills, and contact your healthcare provider if they occur.
Your doctor will provide specific instructions regarding activities and follow-ups, typically advising you to avoid strenuous exercise for at least 24 hours.
Your doctor will give you specific guidelines, often recommending that you refrain from strenuous exercise for at least 24 hours.
Results from the amniocentesis usually take one to two weeks, during which you may feel anxious. Your healthcare provider will discuss the findings and any necessary next steps based on the results.
Stay in touch for support and further questions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Does Amniocentesis Typically Cost?
Amniocentesis typically costs between $1,000 and $3,500, depending on your location and insurance coverage. It’s essential to check with your healthcare provider and insurance company for specific pricing and potential out-of-pocket expenses.
Can Amniocentesis Be Done at Any Stage of Pregnancy?
You can typically perform amniocentesis between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy. Doing it earlier or later isn’t standard practice, as the procedure is most effective and safe within this specific timeframe.
Will I Feel Pain During the Amniocentesis Procedure?
You might feel a brief pinch, like a mosquito bite, during the amniocentesis. Most people describe it as mild discomfort rather than pain. Your healthcare provider will guide you through the process for reassurance.
What Happens to the Amniotic Fluid After Testing?
After testing, the amniotic fluid is typically discarded. However, some facilities may store samples for further research or analysis if needed. You won’t retain any of the fluid post-procedure, ensuring no risk of complications.
Are There Alternatives to Amniocentesis for Genetic Testing?
Yes, there are alternatives to amniocentesis for genetic testing, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT). These options can provide valuable information with different levels of risk and accuracy.
Conclusion
To summarize, amniocentesis can be a valuable tool in evaluating fetal health and genetic conditions during pregnancy. For instance, a couple, Sarah and Jake, chose to undergo the procedure after receiving a positive screening for a genetic disorder. The results provided clarity and allowed them to make informed decisions about their baby’s future. Understanding the procedure’s benefits, risks, and expected outcomes can empower you to navigate this pivotal moment with confidence, ensuring you feel supported throughout the process.